Healthcare will always be people-driven at its core. However, technology can aid the dedicated individuals that work in the field by enabling them to provide higher-quality care to their patients.
Furthermore, technology can help fill the gaps where the healthcare system is experiencing shortages. It is estimated that by 2030, the world will need 80 million healthcare workers to sustain the global population. However, according to the World Health Organization, there will be a healthcare worker shortage of roughly 15 million people by that time.
What role do engineers have in addressing the looming labor shortage? Implementing automation in healthcare.
What is Automation in Healthcare?
Augmentation and automation in healthcare describe the collaboration of artificial intelligence with human physicians and clinicians in an effort to improve treatment and ultimately save lives.
Automation in healthcare expedites functions and procedures, allowing clinicians to provide higher quality care on a more widespread scale. The innovations of automation come with remarkable benefits, specifically in the realm of surgery and intervention.
Automation in the Operating Room: Which technology enables surgery to be more precise?
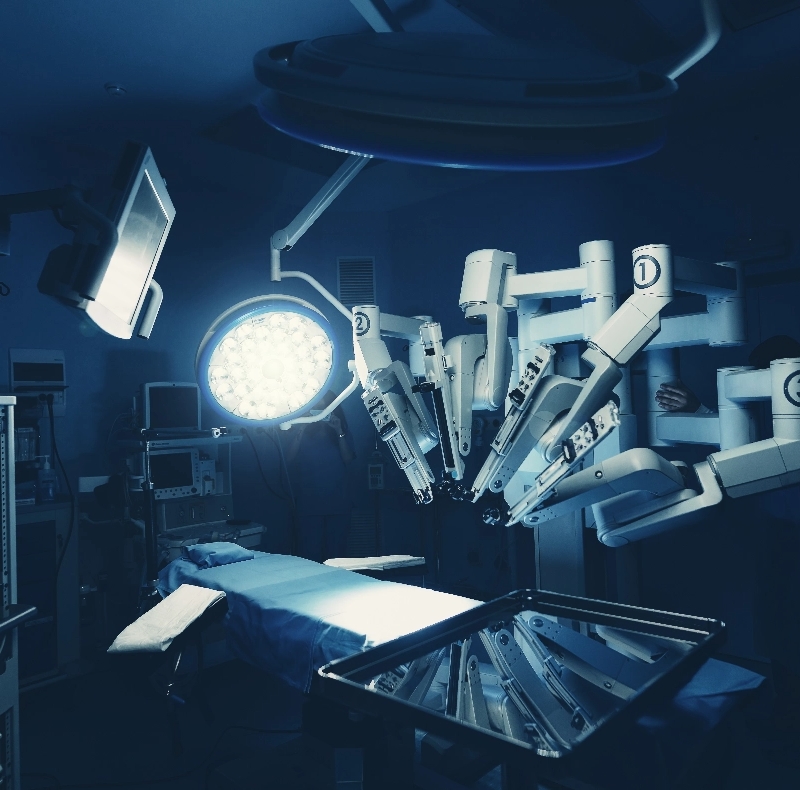
Robot-assisted surgeries (RAS) and minimally invasive surgeries (MIS) are novel advancements in surgery and intervention that enhance the surgeon’s capabilities and level of precision beyond what the body allows. Through this technology, robot-assisted surgeries have proved to cause less damage to the body, less pain, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, and less risk of complications.
Robot-assisted surgery has made major strides since its inception in the mid-1980s. Through the sophistication of ergonomics, computer power and hardware dexterity, robot-assisted surgeries have greatly improved upon accuracy and ability.
For example, the da Vinci system created by Intuitive is an advanced console that human surgeons are able to manipulate during surgery. The system delivers high-definition views that are magnified beyond 10 times what the human eye is capable of seeing. The surgeon maneuvers tiny instruments that wield like a human hand with an impressive range of motion. There is also a built-in tremor-filtration technology that helps steady the instruments for precision.
One common surgery that is often assisted by the da Vinci system is a mitral valve repair—a type of cardiac surgery that fixes or replaces a leaky or stiff mitral valve in the heart. Prior to new technologies, cardiac surgery could only be performed by way of open heart surgery. Open heart surgery requires a large incision down the chest, cutting through the breastbone, and opening the ribcage to view and work on the heart. However, with the robotic assistance from the da Vinci system, this repair only requires a few small incisions which the surgeons use to insert surgical equipment and a camera for viewing.
Between 2001 and 2002, 25 patients underwent robotic mitral valve repair using the da Vinci robotic system. Of all the patients, there were no incisional conversions, deaths, strokes or re-operations for bleeding. 84 percent of patients were extubated in the operating room and 32 percent of patients were discharged from the hospital in less than 24 hours, with an average hospital stay of 2.7 days. In comparison, the average hospital stay for open heart surgery is four to five days.
There was a significant difference in total operating room time from the first 10 patients to the latter 15. The total operating room time for the first 10 patients was 318.5 versus 275.1 minutes for the remaining 15.
The da Vinci system is completely dependent on surgeon control. However, the degrees of autonomy in robotics used in surgery vary with the integration of artificial intelligence. Other surgical robots, like the CyberKnife, are partially autonomous. The CyberKnife's robotic arm moves around the patient, distributing radiation as the healthcare provider remains in the other room monitoring its progress.
The Benefits of Incorporating AI Into Surgery Technology
The future of AI in surgery offers an optimistic path forward in which technology and surgeons can work in tandem, enhancing the powers of the human mind. Artificial intelligence is a broad phrase for computer systems that can perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as visual perception, decision-making, speech recognition, and translation between languages.
Human surgeons juggle a set of physical, mental and technical variables during surgery that all contribute to the success of each procedure. Fatigue, tremors and mental blocks all have the capacity to affect the outcome of the surgery. However, future advancements of AI may help surgeons keep these factors consistent and predictable.
Conventional surgical robots are used for their advantages over human surgeons to improve upon these variables. For example, robots are fatigue and tremor resistant, have scalable motion and work with a greater range of axial movement. These abilities have been demonstrated to produce enhanced margins and lower morbidity rates.
Furthermore, the combination of AI algorithms with surgical robots can elevate surgery and procedures even further by:
- Reducing technical errors and operative times
- Enhancing access to hard-to-reach body areas
- Improving outcomes by removing (or reducing) the potential for human error
Researchers are also exploring the use of AI in surgery for real-time image-based analysis in applications including computer-aided diagnosis, image-guided surgery, and virtual colonoscopy. Though still in its infancy, predictive video analysis could be used to identify or predict adverse events in real-time for intraoperative clinical decision support. This could equip surgeons with active prediction and model surgical risk to determine the optimal type of intervention.
These future possibilities of automation in healthcare and AI in surgery and intervention will be made possible by engineers trained in this highly-specialized field of study. The master of surgery and intervention program at Vanderbilt University places students on the cutting edge of innovation where technology and medicine meet.
Are you ready to turn future possibilities into present-day practices? Contact our graduate admissions office.
Ready to take the next step? Request more information today!